Services
Some of the Treatments for Fibroid Vs UFE
Medications
- Oral contraception medications have been used to control the heavy bleeding.
- (GnRH family) have been used to control the symptoms, with often poor patients’ compliance secondary to unwanted side effects such as hot flashes, hair loss, etc.
- Progestin releasing Intrauterine Device (IUD)
- Hormone Modulators are other modalities to control the symptoms.
Hysterectomy
Is a major surgery entails removing the whole uterus and/or cervix with subsequent side effects. Hysterectomy requires general anesthesia, long hospital stay, and long recovery period. Women can NO longer have children. The most common complications of hysterectomy can be summarized by infections, venous thromboembolic, genitourinary, gastrointestinal tract injury, bleeding, nerve injury, and vaginal cuff dehiscence, The incidence of these complications varies depending on the route and technique of surgery, to list few complications due to surgery:
- Infections
- Venous thrombosis (vein clot/ thrombus).
- Injury to the bowel, bladder and ureters.
- Hemorrhage rarely requires blood transfusions.
- Nerve Injury.
- Vaginal cuff dehiscence (non-healing of the sutured end of the vagina, more prevalent with total laparoscopic hysterectomy.
- Anesthesia complications.
- Menopause (ovarian failure) occurs within five years of the hysterectomy, one or both ovaries may become nonfunctional because of disruption of their blood supply following hysterectomy.
- Decreased libido and low sexual enjoyment. This could be related to loss of the uterine contractions during orgasms. Another factor is vaginal dryness associated with ovarian failure.
Myomectomy
It is one of the surgical uterus-sparing option. Myomectomy is surgical removal of the fibroids. The route and technique of the surgery (large incision, Laparoscopic, transvaginal) depends on the location and size of fibroids. For example, submucosal fibroid can be removed via transvaginal approach using hysteroscope.
The disadvantages of myomectomy:
- Requires of general anesthesia for certain routes.
- Can’t treat all fibroid in one session.
- Larger fibroids increase the risk of converting myomectomy to hysterectomy.
Endometrial ablation
Is used to ablate the inner lining of the uterus and is not used to treat fibroids.
Radio-Frequency Ablation
Is a surgical technique that involves laparoscopic delivering high killing temperature to the fibroid. The procedure requires general anesthesia and is not recommended for large fibroids. In additions, RF ablation only treats a limited number of fibroids same as myomectomy.
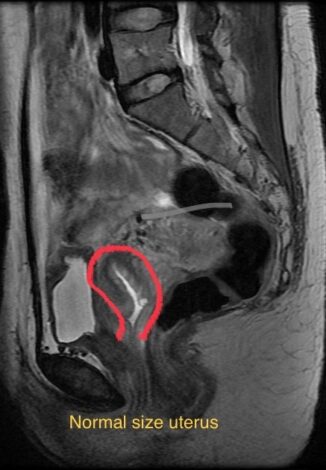
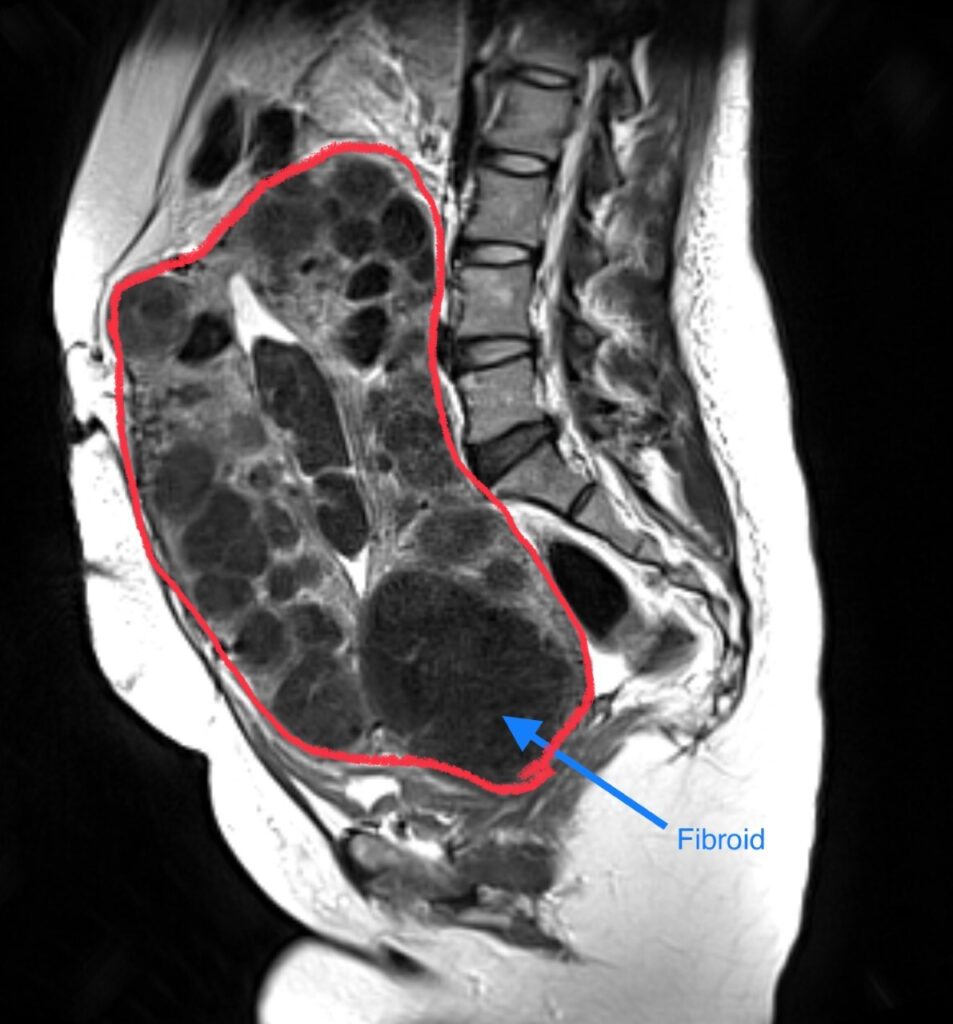
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
Among the best non-surgical options to treat symptomatic fibroids. Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure is being performed as an outpatient in office-based setting.
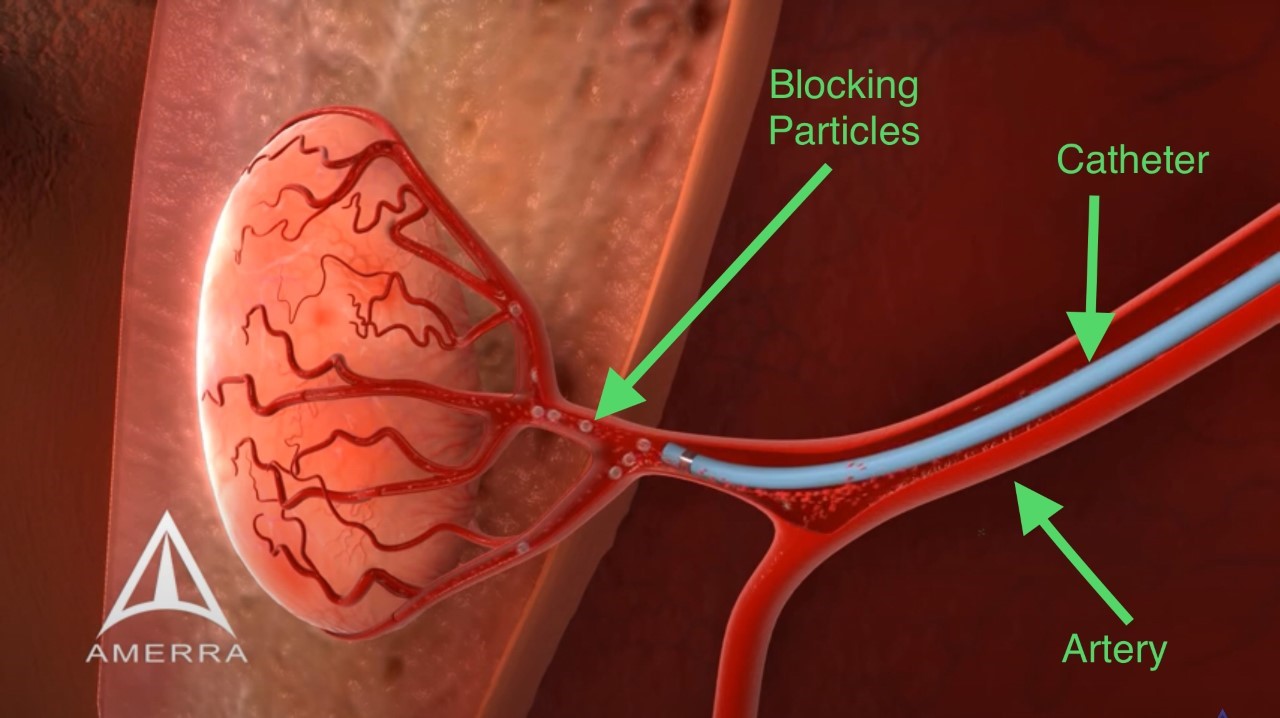
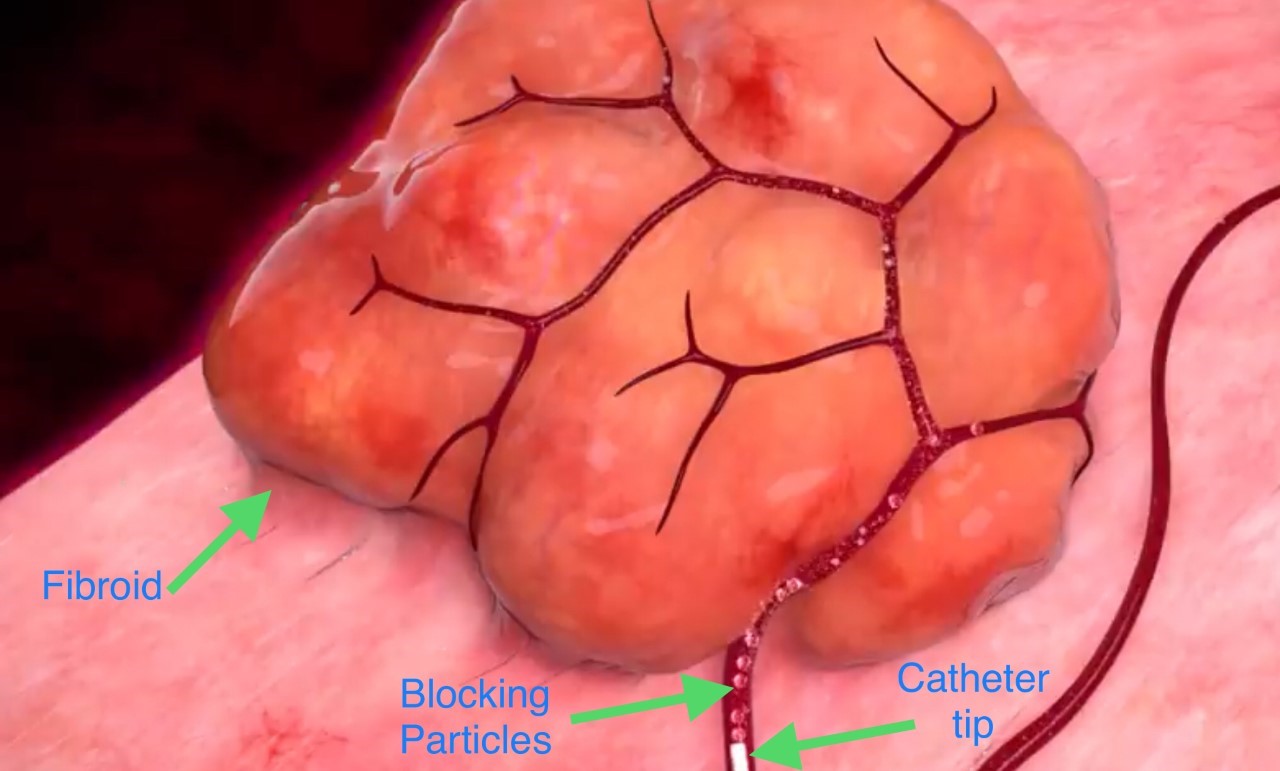
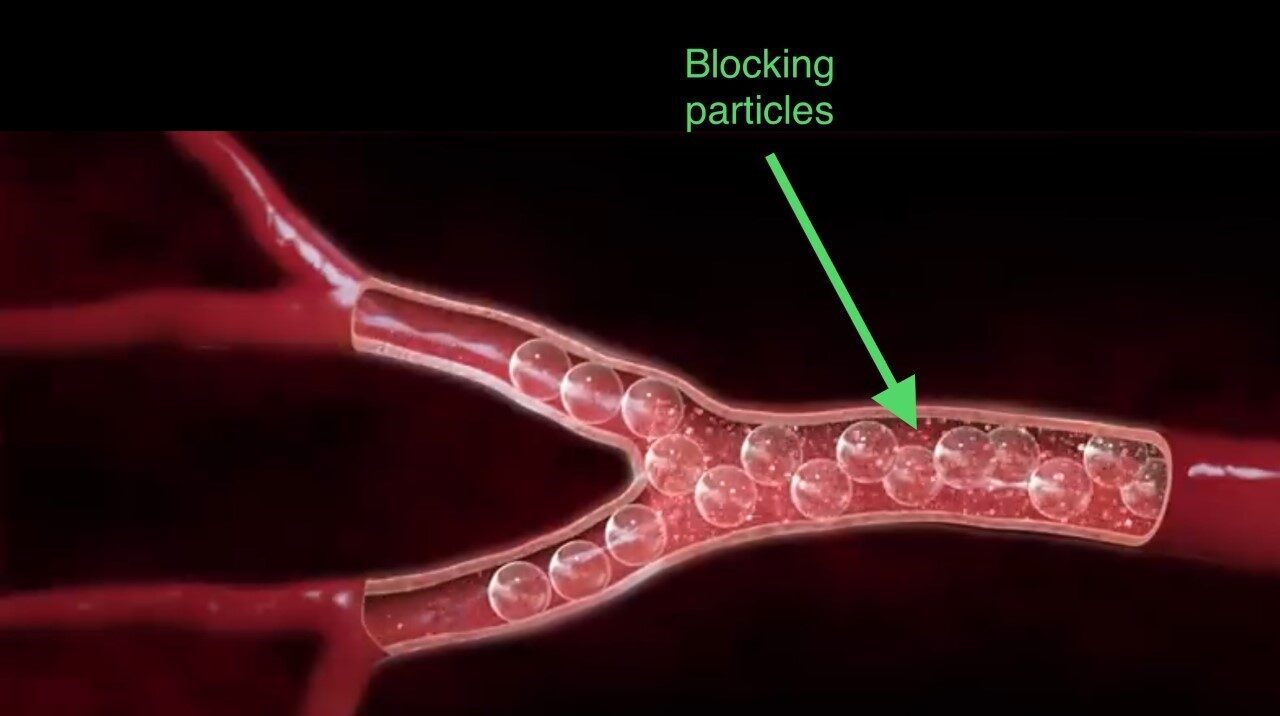
The Interventional radiologist advances the catheter towards the artery (under X-Ray guidance) that is feeding blood to the uterine fibroid. Then, small blocking/embolic particles are delivered via the catheter and tightly packed into the artery. This process (embolization) stops the blood flow to the fibroid and ultimately the fibroid shrinks in size and becomes less symptomatic. The procedure time is usually 45-60 minutes. Women usually resume their daily activities in 2 weeks, sexual activity after 3 weeks, and pregnancy after 6 months pending discussion with their physicians.
The advantages of UFE are:
- Safer when compared to hysterectomy.
- No general anesthesia when compared to myomectomy.
- Short Recovery when compared to hysterectomy.
- No general anesthesia when compared to myomectomy.
- No blood loss and possible need for blood transfusion when compared hysterectomy or myomectomy.
- Treat all fibroids in the uterus in the same procedure when compared to myomectomy.
- Less risk of recurrence when compared to myomectomy.
Below are three animated photos summarizing the UFE procedure. The photos show the blocking agents are packed in the artery and hence no blood reaches the fibroid.
The disadvantages or risks of UFE are:
- Contrast Dye Allergy rarely occurs with angiography procedure and the incidence ranges (0.02% - 0.4%). Patients are usually treated with medication before the procedure and do well.
- Hematoma at the puncture site, and the incidence is 0.2%.
- Other complications are related to the location of the fibroids. These are the pedunculated submucosal fibroids (least frequent). These types of fibroids might fall in the lumen of the uterus post UFE and invariably, they are uneventfully expelled as pieces from the uterus. On few occasions if the slough fibroid is too large to pass, the gynecologist extracts the sloughed fibroid with a simple D&C curettage.
- Menopause is seen in women with older age (>40 years). Around 2% of women experience menopause after UFE procedure.
Contact Us
-
411 N central Avenue, Suite 200,
Glendale, CA 91203 - (818)745-6463
- californiaFibroid@gmail.com

© 2022 California Vascular Health Institute, LLC | Powered by Networkpouch.com